
Satellite launches have become a cornerstone of modern technological advancement, driving innovation in communication, navigation, earth observation, and scientific research. In 2023, Europe made significant strides in the space sector, contributing to global space exploration efforts with numerous successful satellite launches. This article delves into the top 10 European satellite launches of the year, highlighting their purposes, specifications, and broader impact.
Overview of Satellite Launches in 2023
Technological Advancements
2023 witnessed remarkable advancements in satellite technology, including enhanced payload capacities, improved propulsion systems, and advanced onboard sensors. These innovations have enabled satellites to perform more complex tasks, offer better data resolution, and ensure longer operational lifespans. European space agencies and companies have been at the forefront of these technological developments, driving forward global satellite capabilities.
Key Players in the European Space Sector
Several key players have emerged as leaders in the European space sector, including the European Space Agency (ESA), Arianespace, and national space agencies such as CNES (France), DLR (Germany), and the UK Space Agency. Private companies like Airbus, Thales Alenia Space, JSC Reshetnev, and OneWeb have also played crucial roles in the success of European satellite missions.
Detailed Analysis of Top 10 European Satellite Launches
Launch #1: Eutelsat Konnect VHTS
Purpose and Specifications
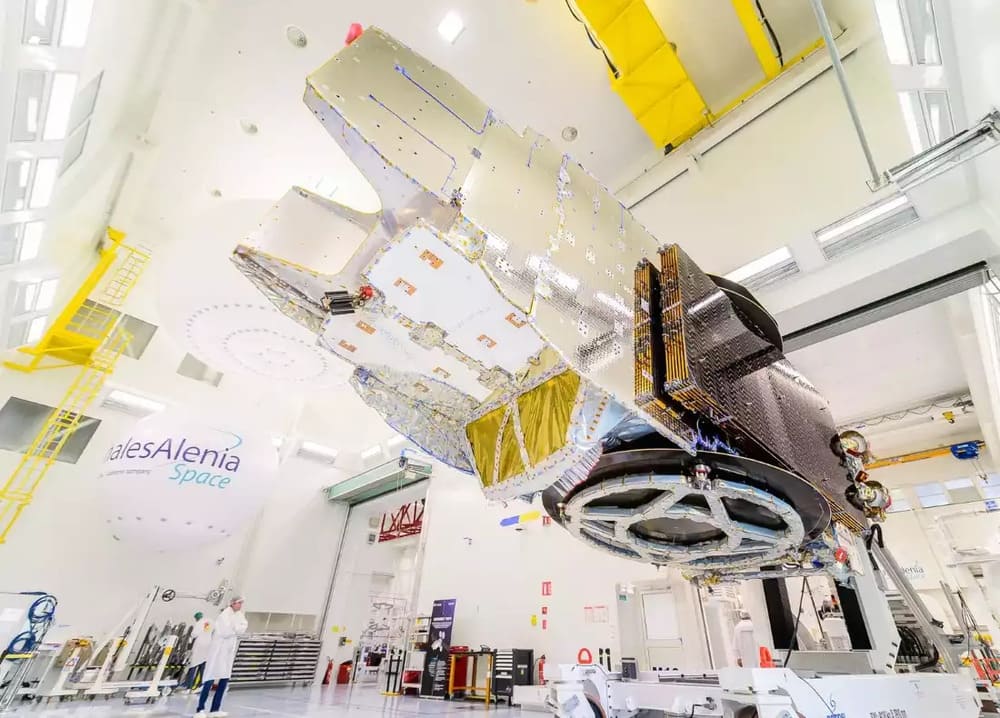

Eutelsat Konnect VHTS (Very High Throughput Satellite) is designed to provide high-speed internet services across Europe, offering unprecedented connectivity and bandwidth. This satellite aims to bridge the digital divide by delivering internet access to remote and underserved areas.
Launch Details and Timeline
Launched in March 2023 aboard an Ariane 5 rocket from the Guiana Space Centre, Eutelsat Konnect VHTS is expected to significantly enhance internet service provision across Europe, supporting both individual users and businesses.
Launch #2: Galileo FOC-M9
Purpose and Specifications
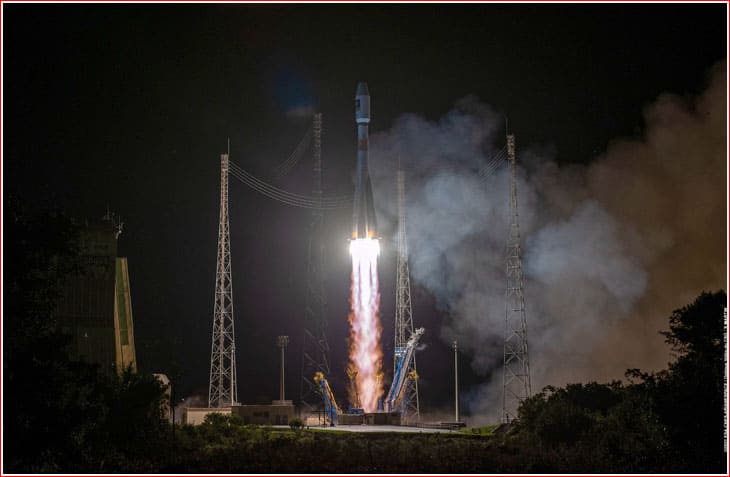

Galileo FOC-M9 is part of the Galileo satellite navigation system, Europe’s answer to the US GPS and Russia’s GLONASS. This satellite enhances the accuracy and reliability of navigation services provided by the Galileo constellation.
Launch Details and Timeline
The satellite was launched in June 2023 using a Soyuz rocket from the Guiana Space Centre. It plays a critical role in expanding the Galileo network, improving positioning services for a wide range of applications, from navigation to emergency response.
Launch #3: Sentinel-6B
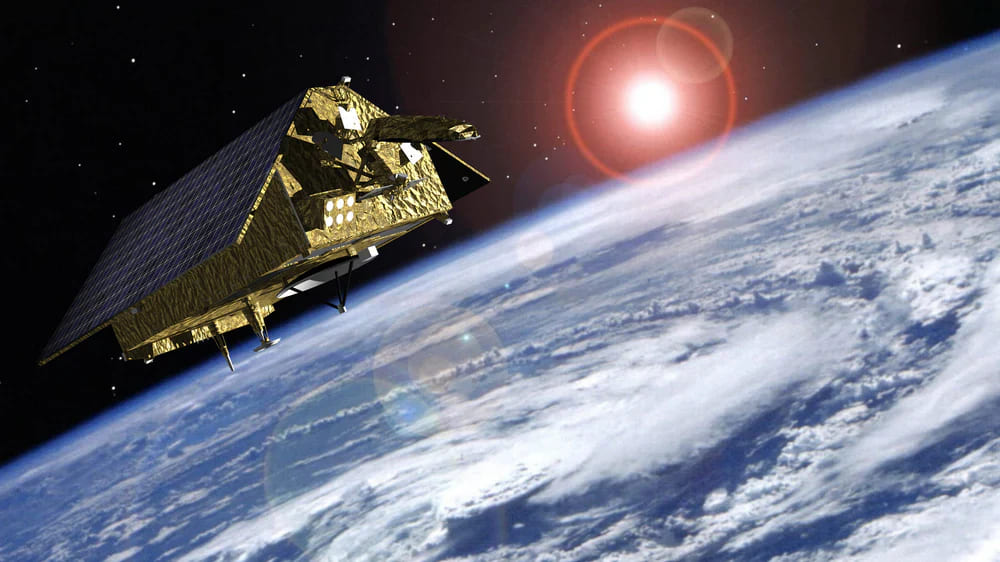

Purpose and Specifications
Sentinel-6B is part of the Copernicus program, aimed at monitoring sea level rise and providing essential data for climate change studies. Equipped with advanced radar altimetry, it offers precise measurements of sea surface height, wave heights, and wind speed.
Launch Details and Timeline
Sentinel-6B was successfully launched in September 2023 aboard a Falcon 9 rocket from Vandenberg Space Force Base. Its data is vital for climate scientists and policymakers working on climate change mitigation and adaptation strategies.
Launch #4: OneWeb Constellation
Purpose and Specifications
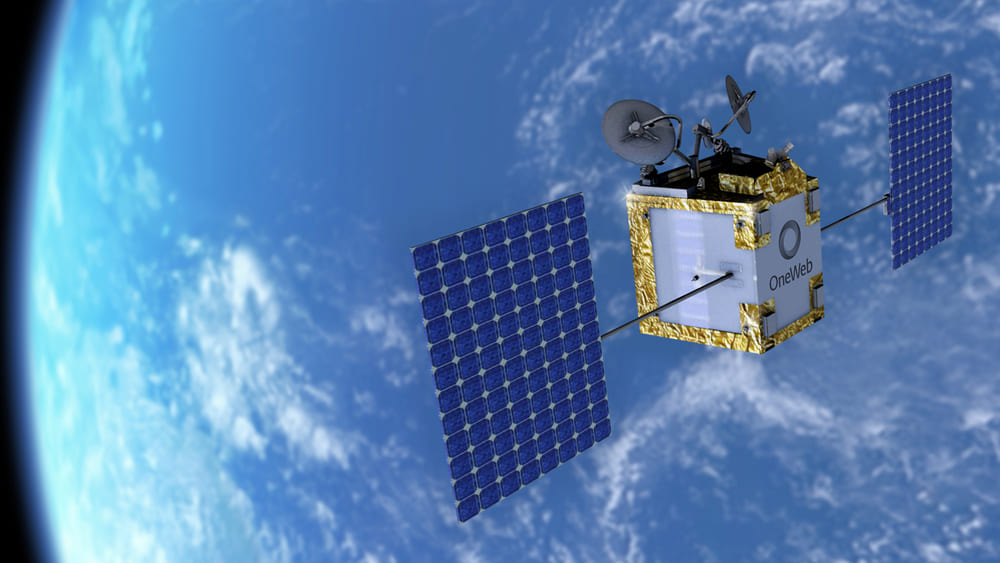

OneWeb’s satellite constellation aims to provide global internet coverage, with a focus on remote and underserved regions. Each satellite in the constellation is designed to deliver low-latency broadband services.
Launch Details and Timeline
In 2023, several OneWeb satellites were launched from the Baikonur Cosmodrome using a Soyuz rocket. This ongoing project is critical in achieving OneWeb’s goal of providing comprehensive global internet coverage.
Launch #5: EnMAP
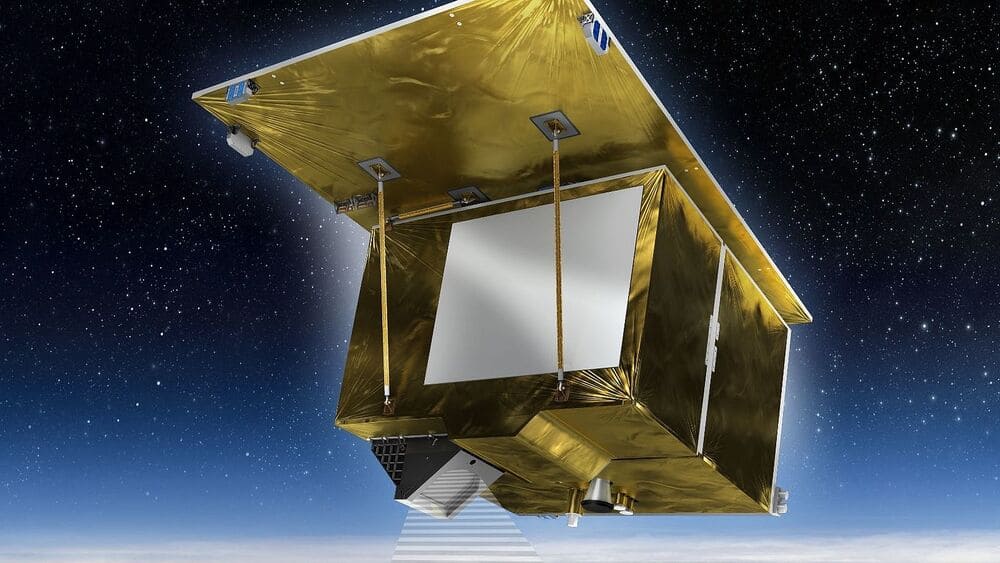

Purpose and Specifications
The Environmental Mapping and Analysis Program (EnMAP) satellite is designed to monitor and analyze Earth’s environment, focusing on vegetation, soil, and water quality. It features a hyperspectral imager capable of capturing detailed images across a wide spectrum of wavelengths.
Launch Details and Timeline
EnMAP was launched in April 2023 on a Falcon 9 rocket from Cape Canaveral. Its data is essential for environmental monitoring, agricultural management, and natural resource exploration.
Launch #6: Biomass PFT
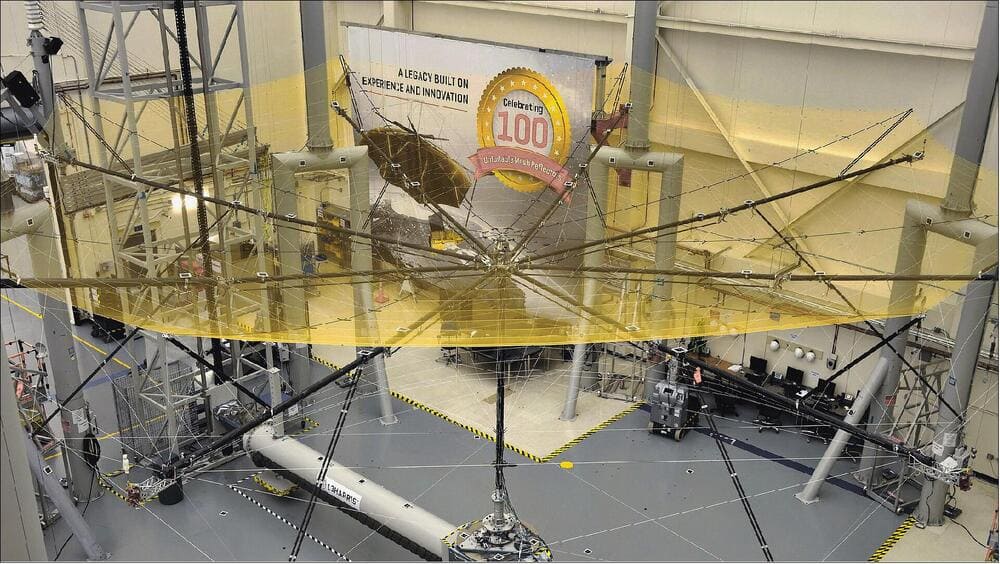

Purpose and Specifications
The Biomass PFT (Planned Flight Test) satellite is part of ESA’s Earth Explorer missions, aimed at mapping forest biomass to better understand the carbon cycle and forest dynamics. It carries a novel P-band synthetic aperture radar.
Launch Details and Timeline
Biomass PFT was launched in July 2023 from the Guiana Space Centre using a Vega rocket. It provides critical data for climate research and forest management practices.
Launch #7: METEOSAT Third Generation
Purpose and Specifications
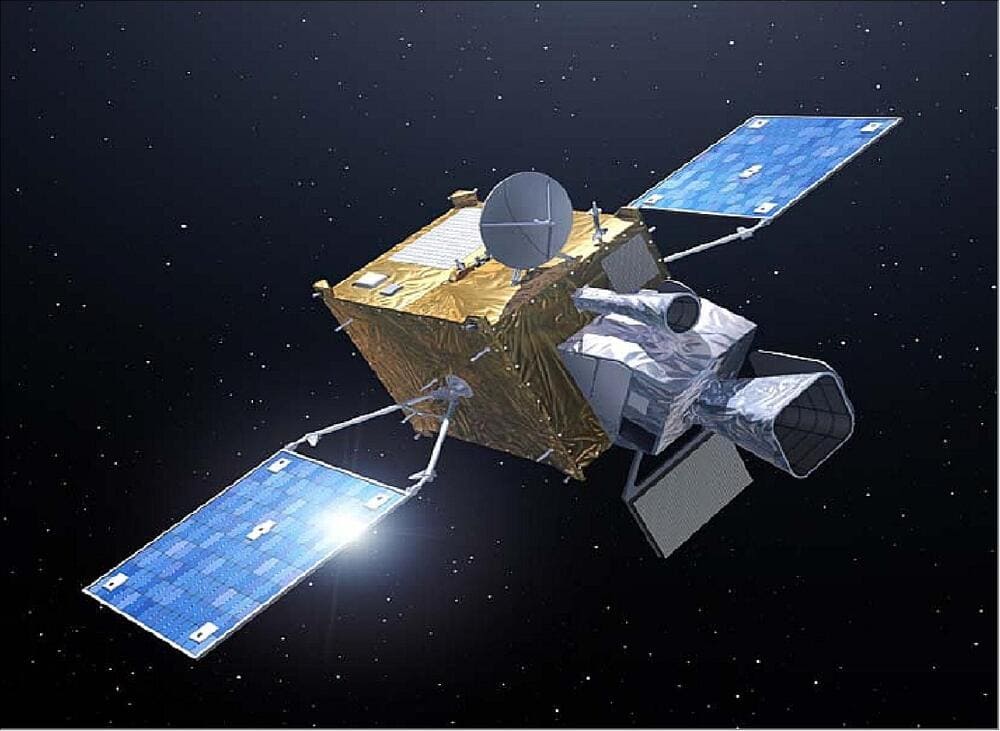

The METEOSAT Third Generation (MTG) satellite series is designed to provide improved weather forecasting and climate monitoring. These satellites offer higher resolution imaging and more frequent observations than their predecessors.
Launch Details and Timeline
MTG-I1, the first satellite of this new generation, was launched in December 2023 aboard an Ariane 6 rocket from the Guiana Space Centre. It enhances Europe’s capability in weather prediction and climate monitoring.
Launch #8: CSO-3
Purpose and Specifications
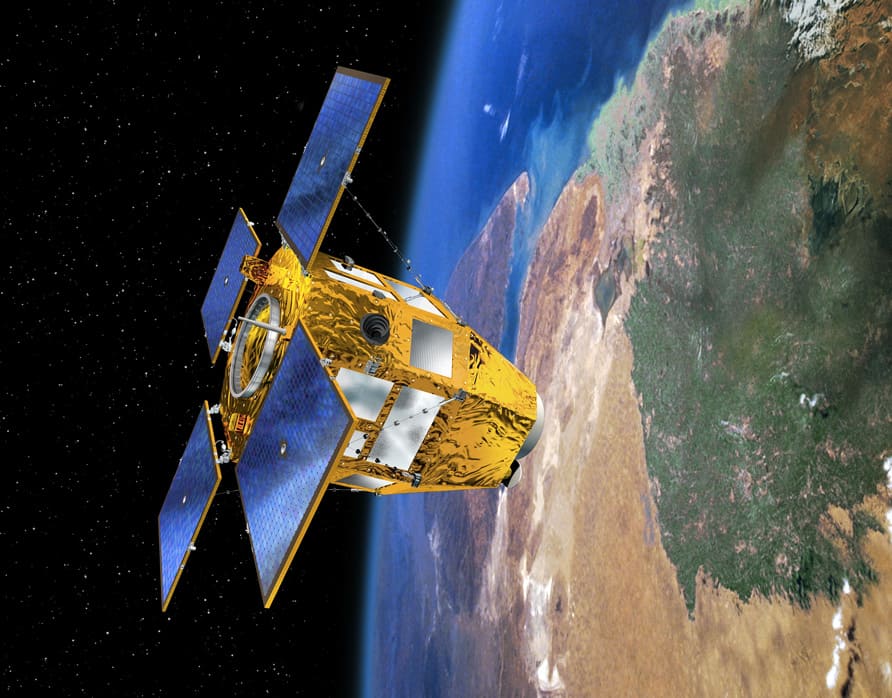

CSO-3 (Composante Spatiale Optique) is part of France’s military observation satellite program, providing high-resolution imagery for defense and security applications. It features advanced optical sensors for detailed earth observation.
Launch Details and Timeline
Launched in May 2023 on a Soyuz rocket from the Guiana Space Centre, CSO-3 enhances France’s reconnaissance and surveillance capabilities.
Launch #9: IOD-3 Amber
Purpose and Specifications
IOD-3 Amber is a part of the In-Orbit Demonstration program, aimed at testing new technologies and applications in space. It focuses on maritime domain awareness, tracking ships, and monitoring illegal activities at sea.
Launch Details and Timeline
The satellite was launched in August 2023 on a PSLV rocket from India. Its successful deployment marks a significant step in advancing maritime security technologies.
Launch #10: ARIEL
Purpose and Specifications
ARIEL (Atmospheric Remote-sensing Infrared Exoplanet Large-survey) is a mission led by ESA to study the atmospheres of exoplanets, aiming to understand their formation and evolution. It carries a suite of spectrometers and photometers.
Launch Details and Timeline
Scheduled for launch in late 2023 on an Ariane 6 rocket from the Guiana Space Centre, ARIEL will investigate the atmospheres of hundreds of exoplanets, providing insights into their chemical composition and potential habitability.
Impact of These Launches
Scientific Advancements
These satellite launches contribute significantly to scientific research, providing critical data for climate studies, environmental monitoring, and space exploration. They enhance our understanding of earth systems, weather patterns, and the universe beyond.
Economic Benefits
The successful deployment of these satellites stimulates economic growth by fostering innovation, creating jobs, and driving advancements in technology. Improved communication and navigation services also support various industries, from agriculture to transportation.
Enhancing European Space Capabilities
These launches bolster Europe’s position as a leader in space technology, showcasing its ability to develop and deploy advanced satellites. This enhances collaboration opportunities with other space-faring nations and contributes to global space exploration efforts.
In 2023, Europe’s space sector achieved remarkable milestones with the launch of several advanced satellites. These missions not only enhance technological capabilities but also contribute to scientific research, economic growth, and environmental monitoring. Looking forward, the continued success of European satellite launches promises even greater advancements in space technology and exploration.
FAQs
What are the key achievements of European satellite launches in 2023?
The key achievements include significant advancements in communication, navigation, earth observation, and scientific research, with the successful deployment of technologically advanced satellites like Eutelsat Konnect VHTS, Galileo FOC-M9, and ARIEL.
How do these launches benefit everyday life?
These satellite launches improve internet connectivity, enhance navigation services, provide critical environmental data, and support weather forecasting, all of which have direct and indirect benefits on daily life.
What are the challenges faced by European satellite missions?
Challenges include technological complexities, high costs, regulatory hurdles, and the need for international cooperation. Ensuring the reliability and longevity of satellites in the harsh environment of space is also a significant challenge.
How does Europe compare to other regions in space technology?
Europe is a leading player in space technology, comparable to the US, Russia, and China. The European Space Agency and private companies have made significant contributions to global space exploration and satellite technology.
What can we expect from European satellite launches in 2024?
In 2024, we can expect continued innovation and more ambitious missions, including further advancements in earth observation, communication, and scientific research. New launches will likely build on the successes of 2023, driving forward Europe’s space capabilities.












